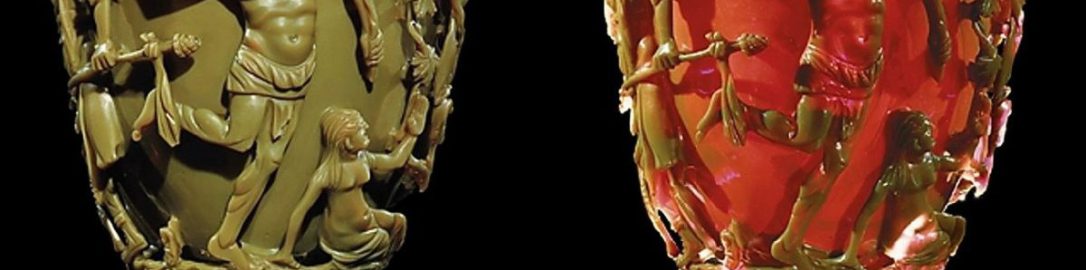
Lycurgus Cup (also known as the Lycurgus chalice) is an example of the advancement of Roman culture. Depending on the angle at which the sun’s rays fall on the cup, the decorations of the vessel change in different colours. When lit from the front, they are green. However, with light coming from the rear, they turn red. Thus, it can be said that the Romans were pioneers of nanotechnology!
The ancient artists who made the chalice crushed ordinary glass particles with gold and silver particles to create granules with a diameter of only 50 nanometers. From the mixture prepared in this way, they created the so-called dichroic glass, i.e. glass whose perceived colour varies depending on the angle of viewing and incidence of light.