Chapters
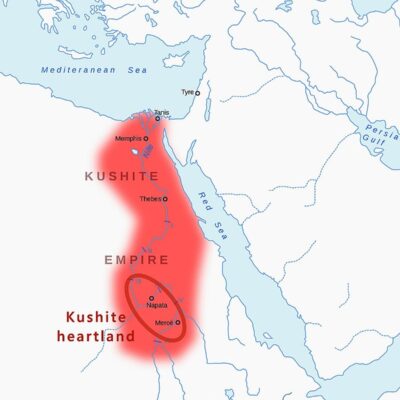
Kingdom of Kush, also called Nubia, located south of Egypt, was one of the most powerful African kingdoms of antiquity, stretching across modern-day Sudan. Its history dates back to the second millennium BC, and in 747 BCE the rulers of Kush even conquered Egypt, creating the so-called Twenty-fifth Dynasty, called the “Nubian Dynasty”. The Romans took control of Egypt after the defeat of Cleopatra and Mark Antony in 30 BCE, which meant new challenges and opportunities for Cush, whose relations with Rome were complex and turbulent.
Beginnings of relations between Kush and Rome
After the Romans took over Egypt, Kush had to re-establish its relations with its new neighbour to the north. The first contacts between Rome and Cush were tense, and Roman troops quickly encountered resistance from the Nubians. Conflicts over border areas were not uncommon – the Romans tried to maintain control over northern Egypt, which required constant vigilance from the Kushites.
Battle of Qasr Ibrim and establishment of borders
The greatest point of contention between Rome and Cush was Lower Nubia, located on the border between the two countries. In 23 BCE the Nubians attacked Roman garrisons in the region, leading to the clash at Qasr Ibrim. Although the Nubians were initially successful, the Romans quickly responded by conquering Meroë, the then capital of Kush. However, due to logistical difficulties and the hot climate, the Roman army withdrew, which led to the signing of a treaty that stabilized the borders for a long time and ended the wars between the two countries.
Queen Amanirenas, who successfully faced Rome, is considered a symbol of the independence of Kush. The cult of Amun was strongly developed in Nubia, and after conquering Egypt, the Kushites transplanted the cult of Amun to Upper Egypt. In return, Rome brought influences from Hellenistic culture, and thanks to trade relations, Roman influences penetrated everyday life in Kush. Nevertheless, Kush remained true to its culture, which expressed its unique identity.
Diplomacy and trade
After initial clashes, relations between Rome and Cush began to stabilize. Trade flourished in the Kushite cities, where Rome played a significant role. Exotic goods passed through the Nubians – ivory, gold, exotic wood and slaves – and ended up on the Roman market. The Romans, in turn, provided the Kushites with luxury goods, such as glassware and jewellery. Despite different cultures and languages, both countries were able to establish beneficial cooperation based on the exchange of goods and experiences.