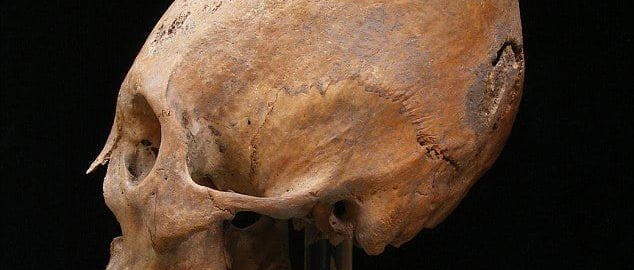
Scientists from the University of Cambridge analyzed human remains – dated to the 5th century CE – from the Roman frontier region of Pannonia (present-day Hungary). Research results show that some Roman citizens abandoned their farms and adopted the nomadic lifestyle from the Huns.
The analysis of teeth and bones allowed archaeologists to assess that the diet of the Romans was largely based on meat and fish. Typical Roman farmers, on the other hand, ate mainly grain, vegetables, bread and a little meat, without fish. Interestingly, some of the Huns took over the settlement lifestyle from the Romans and set up their own farms.
According to Dr Susanne Hakenbeck, the research results prove that the population living in the border area tried to cope with unfavourable war conditions and coexist.