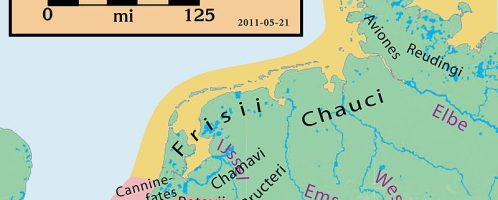
Roman campaigns in Germania (Germania Magna) in time of Octavian Augustus
(16 BCE - 16 CE)
Roman Empire for most of its existence based its borders in Europe on two great rivers: the Rhine and the Danube. Beyond this border, for a long time under Roman rule, there were lands between the sources of these two rivers, the so-called Agrii Decumates and Dacia in today's Romania.