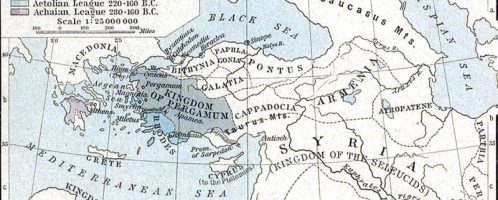
Invasion of Cimbri and Teutons
(109-101 BCE)
Invasion on Italy by Cimbrii and Teutons took place in 109-101 BCE, when the Germanic tribes were forced to leave their homes and seek a new homeland. The great mass of people and determination were to put Rome in great danger.